Why are Manhole Covers Round?
1 February 2024
8 Best Ways to Clear a Drain Pipe
1 April 2024Attenuation Ponds – What They Are & How They Work

Attenuation ponds, a crucial facet of modern water management, play a pivotal role in safeguarding our communities from flooding and water pollution.
These are often overlooked and embody a strategic approach to harmonising urban development with environmental responsibility.
This article delves into the fundamental role these engineered structures play in reshaping urban landscapes.
Understanding what they are, why they are necessary, how they function, and their alternatives is vital for sustainable urban development.
Table of Contents
What are Attenuation Ponds?
Attenuation ponds, also referred to as rainwater attenuation basins, are engineered structures designed to manage and control excess rainwater and help prevent flooding.
These ponds act as temporary reservoirs, strategically placed to collect and detain rainwater runoff.
Positioned strategically across urban landscapes, attenuation ponds function as ephemeral reservoirs, intentionally positioned to intercept and detain the swift flow of rainwater runoff, to help stop waterlogging..
Unlike traditional ponds, attenuation ponds aren’t designed for permanent water storage.
Instead, they emerge as tactical solutions, adept at impeding and regulating the release of surplus water.
These ponds become integral components of the modern urban environment.
Why are Attenuation Ponds Needed?
Attenuation ponds stand as indispensable elements in contemporary urban planning, addressing critical challenges posed by rapid urbanisation and the proliferation of impervious surfaces.
Urbanisation and Impervious Surfaces

Attenuation ponds are used due to urbanisation
With the relentless growth of urban areas, the natural landscape that once facilitated rainwater absorption is replaced by impervious surfaces like roads and buildings.
This transformation disrupts the natural drainage system, leading to increased risks of flooding and water pollution.
Water Management
Attenuation ponds emerge as essential components in the broader strategy of water management.
They act as controlled reservoirs, strategically positioned to collect and temporarily detain water runoff.
This prevents downstream flooding and erosion, safeguarding communities from the adverse effects of uncontrolled rainwater.
Water Quality Enhancement
Beyond flood prevention, attenuation ponds contribute significantly to enhancing water quality.
As rainwater is detained within these ponds, sediments settle, and pollutants are naturally filtered out.
This purification process ensures that the released water is of higher quality, minimising the impact on natural water bodies.
Buffer Against Peak Flows
Attenuation ponds play a crucial role in managing peak flow events during heavy rainfall.
By slowing down the release of rainwater, these ponds prevent sudden surges that can overwhelm drainage systems downstream.
This controlled discharge acts as a buffer, mitigating the risks associated with intense weather events.
Environmental Resilience
Attenuation ponds represent a harmonious integration of urban development and environmental responsibility.
They allow cities to expand while mitigating the environmental consequences of impervious surfaces.
This equilibrium fosters sustainable development, ensuring that urbanisation doesn’t come at the cost of increased flood vulnerability and compromised water quality.
How do Attenuation Ponds Work?
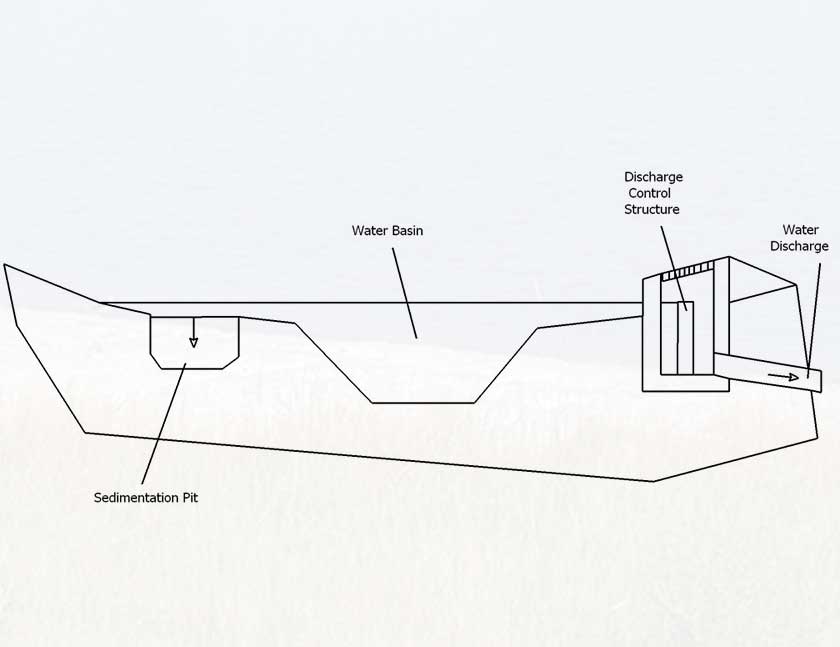
Source: SSWM.info
Attenuation ponds operate on a simple yet effective principle.
When rainfall occurs, water is directed into these ponds, allowing it to accumulate.
The structure dictates the gradual release of accumulated water, ensuring a controlled and measured discharge.
This controlled release mitigates the risk of downstream flooding and erosion, providing a buffer against the sudden influx of rainwater.
The outlet structure, often equipped with features like weirs or controlled pipes, determines the pace of water release.
Moreover, attenuation ponds contribute to water quality improvement.
As water temporarily resides within the pond, sediments settle, and some pollutants are naturally filtered out.
This dual role – preventing flooding while enhancing water quality – defines the effectiveness and significance of attenuation ponds in modern water management.
What Maintenance do Attenuation Ponds Need?
Regular maintenance is crucial for the optimal functioning of attenuation ponds. The most common forms of maintenance are:
Regular Inspection and Monitoring
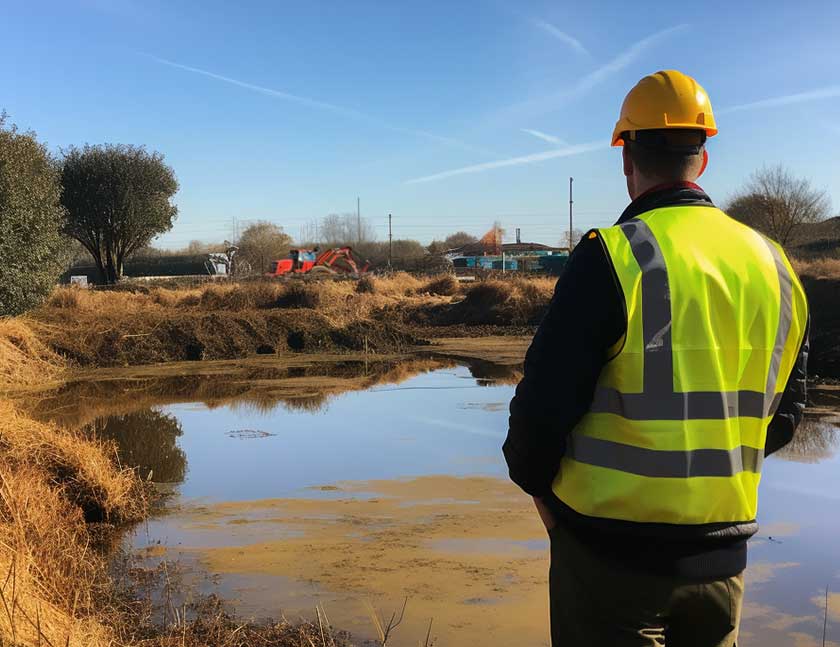

Attenuation ponds need regular inspections
Ensuring the optimal functionality of attenuation ponds requires a diligent regimen of maintenance.
Regular inspections stand as the cornerstone of this process.
Professionals routinely assess the condition of the pond, scrutinising the inlet and outlet structures, embankments, and any vegetation present.
These inspections are crucial for early identification of potential issues that could compromise the pond’s effectiveness.
Sediment Removal and Debris Management
Over time, attenuation ponds accumulate sediment and debris, which can impede their capacity to detain and release water efficiently.
Scheduled sediment removal is, therefore, a critical maintenance task.
Professionals employ various methods, such as dredging or vacuuming, to clear sediments and ensure the pond retains its designed volume.
Vegetation Control
The presence of vegetation in and around attenuation ponds is both beneficial and potentially problematic.
While vegetation aids in natural filtration and erosion control, it needs careful management.
Uncontrolled growth can hinder water flow and impact the pond’s hydraulic efficiency.
Regular trimming and, if necessary, selective removal of vegetation become integral to maintaining the pond’s functionality.
Outlet Structure Maintenance
The outlet structure, including weirs, control pipes, and other components, is pivotal for regulating water release.
Periodic checks and maintenance of these structures are imperative to guarantee their proper functioning.
Any obstructions, damage, or wear and tear must be promptly addressed to uphold the pond’s ability to control rainwater runoff effectively.
Emergency Preparedness
In addition to routine maintenance, a well-thought-out emergency response plan is essential.
Professionals responsible for attenuation ponds should be prepared to address unforeseen issues promptly.
This includes having mechanisms in place to handle extreme weather events, sudden increases in water volume, or unexpected structural concerns.
How do you Build Attenuation Ponds?

This guide will teach the basics on how to build attenuation ponds
Building attenuation ponds involves careful planning and engineering, as well as experienced professionals to ensure the pond is effective and safe.
Site Selection and Planning
The construction of attenuation ponds begins with meticulous site selection and planning.
Professionals carefully evaluate the topography, soil composition, and proximity to urban areas to determine the most suitable location.
The goal is to position the pond where it can effectively intercept and manage rainwater runoff while adhering to environmental and safety regulations.
Excavation and Pond Construction
The physical construction of attenuation ponds involves excavation to create the basin that will hold rainwater temporarily.
This excavation process is conducted with precision to achieve the desired slope and dimensions of the pond.
The excavated material is often repurposed for embankments surrounding the pond, contributing to its structural integrity.
Outlet Structure Installation
A key component of attenuation pond construction is the installation of the outlet structure.
This structure is meticulously designed to regulate the release of water from the pond.
It typically includes features such as weirs, control pipes, or other hydraulic elements that govern the flow of water.
The outlet structure is a critical element in ensuring that water is released gradually to prevent downstream flooding.
Vegetation Incorporation
Vegetation plays a vital role in the functionality of attenuation ponds.
During construction, vegetation is often incorporated strategically to enhance the pond’s ability to filter pollutants and stabilise the soil.
Proper selection and placement of vegetation contribute to the pond’s long-term effectiveness.
Quality Control and Monitoring
Throughout the construction process, quality control measures are implemented to ensure that the attenuation pond meets engineering standards and regulatory requirements.
Continuous monitoring allows for adjustments as needed, ensuring that the pond is constructed to its optimal capacity and functionality.
Integration of Technology
In a modern attenuation pond construction, technology is increasingly integrated for enhanced efficiency and precision.
Geographic Information System (GIS) mapping and other advanced tools aid in the planning and design phases, ensuring that attenuation ponds are strategically placed for maximum effectiveness.
Are Attenuation Ponds the Same as Retention Ponds and Balancing Ponds?
While attenuation ponds, retention ponds, and balancing ponds share similarities, they serve different purposes.
Purpose and Duration
The primary distinction lies in their purpose and the duration for which they hold water.
Attenuation ponds are designed to temporarily hold and gradually release water to prevent flooding during heavy rainfall.
Retention ponds, on the other hand, are intended for more permanent water storage, serving as reservoirs even during non-rainy periods.
Balancing ponds focus on both water quality improvement and controlled water release, often with a heightened emphasis on water treatment.
Water Storage
While attenuation and retention ponds both involve temporary storage, the nature of this storage differs.
Attenuation ponds release water more rapidly, while retention ponds store water for more extended periods, contributing to groundwater recharge and providing a stable water source during dry spells.
Emphasis on Water Treatment
Balancing ponds distinguish themselves through a more pronounced emphasis on water treatment.
They are designed not only to control rainwater but also to enhance water quality through processes such as sedimentation and filtration, ensuring that the released water is of higher quality.
What are the Alternatives to Attenuation Ponds?
There are several modern alternatives to attenuation ponds, each with their own advantages and challenges to overcome.
Permeable Pavement
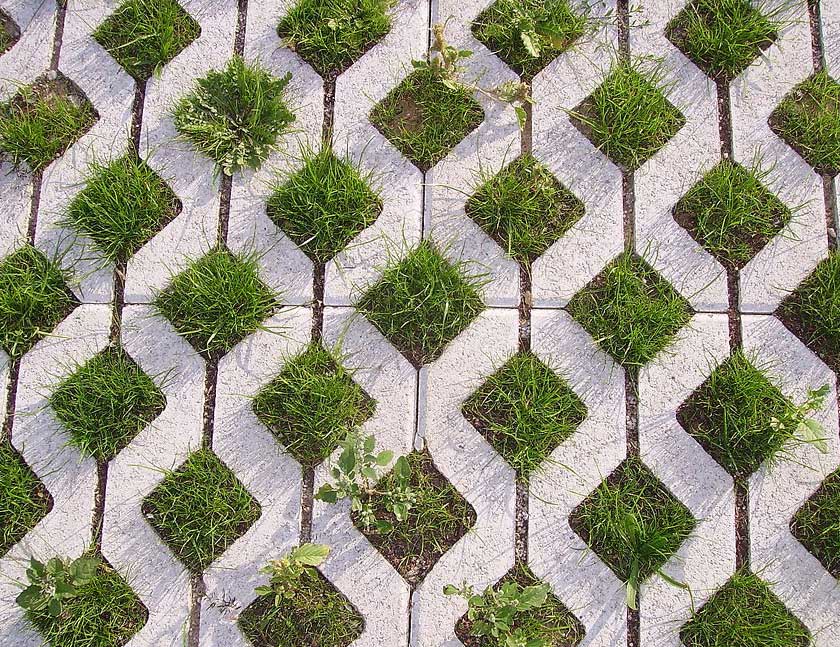

One modern alternative to attenuation ponds is the adoption of permeable pavement.
This innovative solution replaces traditional impervious surfaces like asphalt or concrete with materials that allow water to pass through, reducing surface runoff.
Permeable pavement promotes infiltration, aiding in groundwater recharge and minimising the need for large-scale rainwater management infrastructure.
Green Roofs
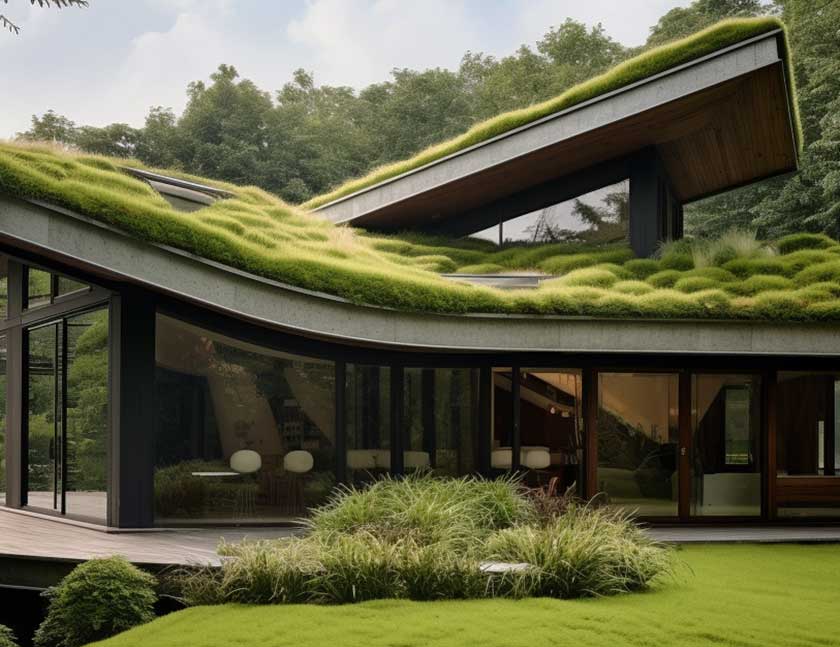

Green roofs offer a nature-based alternative to attenuation ponds.
By covering rooftops with vegetation, these roofs absorb and retain rainwater, reducing the overall volume of water runoff.
Green roofs not only contribute to water management but also provide additional environmental benefits, including improved energy efficiency and enhanced urban biodiversity.
Bioretention Basins
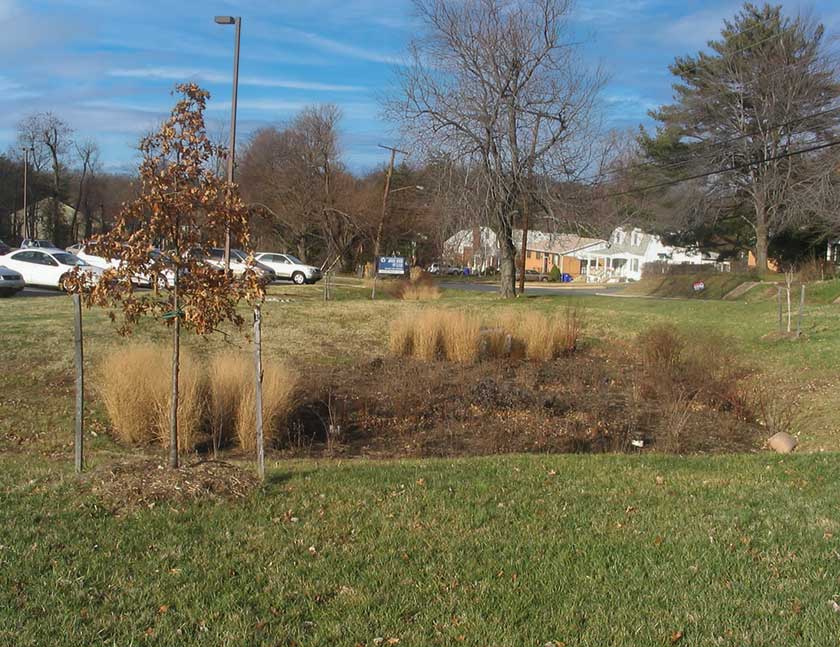

Bioretention basins, also known as rain gardens, are landscape features designed to capture and treat water runoff.
These basins incorporate vegetation and engineered soils to filter pollutants and slow down water flow.
Bioretention basins serve as aesthetically pleasing alternatives that blend into the urban environment while providing effective water management.
Underground Storage Systems
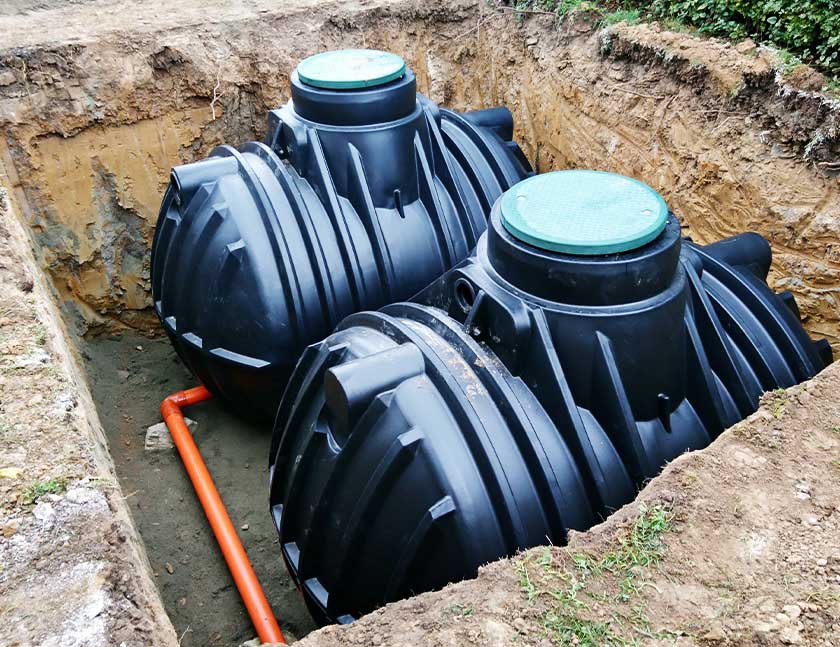

Source: Shutterstock
For areas with limited space, underground storage systems offer a practical alternative.
These systems consist of subsurface chambers or tanks that store rainwater temporarily.
By utilising the underground space, these systems mitigate the impact of urbanisation on natural drainage patterns without the need for visible surface infrastructure.
Swales and Vegetated Channels
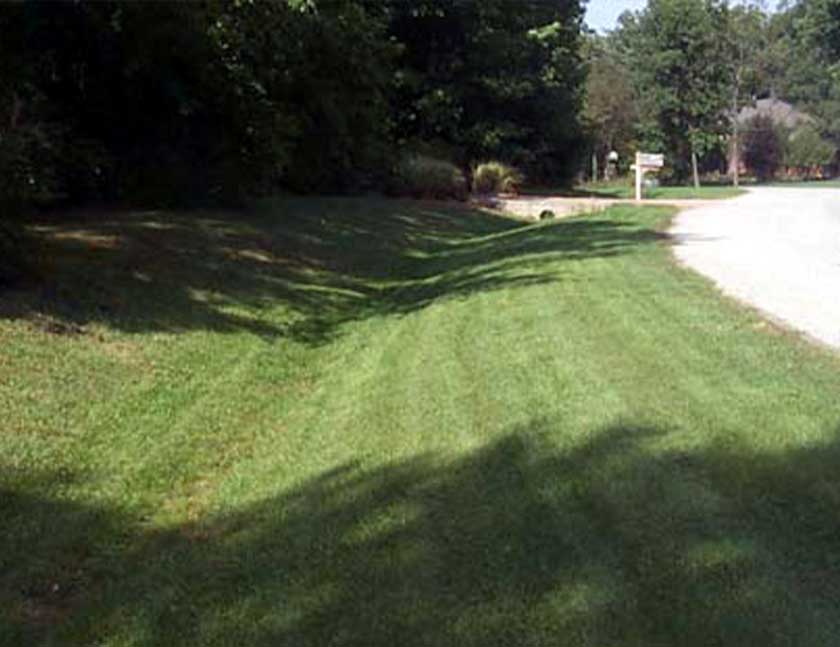

Natural drainage features like swales and vegetated channels represent alternatives that mimic the functions of attenuation ponds.
These landscape elements redirect and slow down water, promoting infiltration and reducing runoff velocity.
Incorporating vegetation in these features enhances pollutant removal and contributes to overall water quality improvement.
Conclusion
Attenuation ponds stand as indispensable components of urban water management, offering a controlled solution to the challenges posed by increased impervious surfaces.
Their role in preventing flooding, improving water quality, and fostering sustainable development cannot be overstated.
As we continue to navigate the complexities of urbanisation, understanding and implementing effective rainwater management practices, including attenuation ponds, becomes paramount for resilient and eco-friendly communities.